Types of Abrasive Materials
March 07, 2023Metal workpieces often contain contaminants or defects that occur naturally or during various manufacturing or processing steps. These imperfections can make it more challenging to apply coatings or execute other essential procedures, reducing the finished product’s quality.
Abrasive blasting effectively removes materials and prepares the substrate’s surface for subsequent production phases. The process involves propelling high-pressure water containing abrasives to blast away dirt, oil, grease, chemicals and other substances to achieve the desired finish.
Numerous abrasive materials, also known as media, are available for the blasting process, each offering specific advantages and disadvantages.
What Are the Different Types of Abrasive Media?
Here’s a closer look at the most common abrasive media types, including a brief description and their typical surface finishing applications:
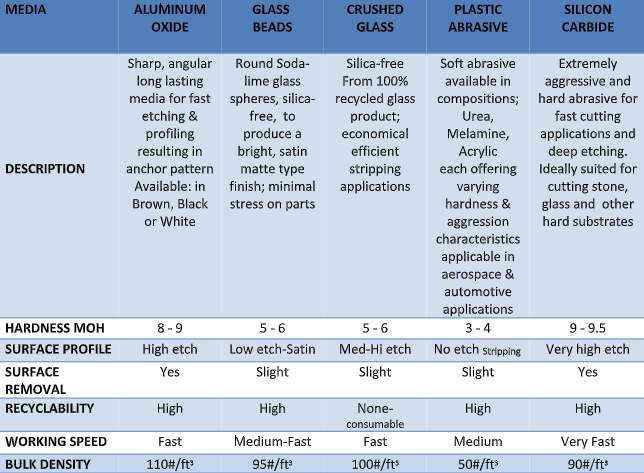
- Glass Beads: Glass is not as aggressive a blasting media as other materials, such as steel shot or silicon carbide. However, it is an excellent choice for applications that require a softer, brighter finish. It is well suited for stainless steel applications. Glass beads can also be recycled multiple times.
- Aluminum Oxide: Aluminum oxide is characterized by its superior hardness and strength. It can be found in applications like anti-slip surfaces, industrial applications as a blasting media and as a raw material in refractories. Aluminum oxide is designed for abrasive pressure blasting of almost any type of substrate: glass, granite, marble and steel. Due to its ability to deeply etch it is used in the preparation of surfaces prior to painting or coatings.
- Plastics: Plastic abrasive is a dry thermoset cleaning media made from crushed urea, polyester or acrylic. Each variety is available in a range of hardnesses and particle sizes. Plastic is generally regarded as the best abrasive material for mold cleaning, blasting of plastic parts or in applications where the removal of the substrate material is not permitted. Common industries that utilize plastic media blasting include automotive, aviation, boating, electronics and industrial applications.
- Silicon Carbide: Silicon carbide is the hardest abrasive blasting material available, making it the best choice for your most challenging surface finishing applications. It is available in various colors and purities. Its primary use ranges from bonded abrasive tools, lapping, polishing, glass etching and general-purpose heavy-duty blast-cutting applications.
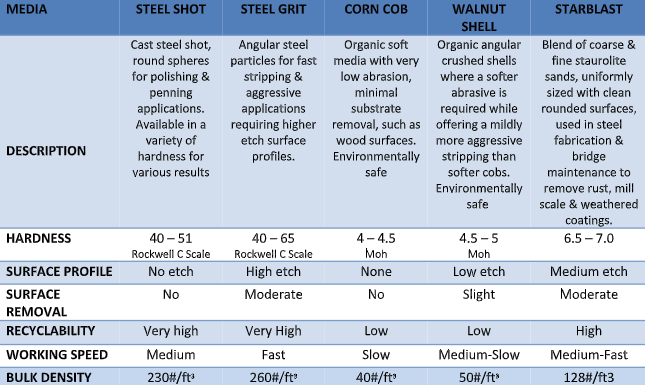
- Steel Shot & Grit: Steel abrasive is a cost-effective alternative to other abrasives due to its toughness and high recyclability. It can be used on a variety of surfaces to effectively remove contaminants, to texture a surface for proper adherence of a final coating or in peening (hardening) applications. The correct size, hardness and shape play a significant role in the proper media selection.
- Starblast: Starblast™ is a mined loose blend of coarse and fine staurolite sands with extremely low levels of silica making it an ideal general-purpose blasting abrasive. It is perfect for removing scale and corrosion from steel surfaces while offering a low dust level for improved visibility.
- Walnut Shells: Walnut shell abrasive is a hard naturally occurring material made from crushed walnut shells. It is the harder of the soft abrasives, available in a variety of sizes for blast cleaning and polishing softer surfaces that could incur damage from harsher abrasives. Typical applications include polishing soft metals, fiberglass, wood, plastic and stone. It can also be used in tumbling operations for polishing gems and jewelry.
- Corn Cobs: Corn cob abrasive is a granular abrasive manufactured by crushing the dense woody ring of a corn cob into various grit sizes. It is the softer of the naturally occurring abrasives making it ideal for cleaning, deburring, burnishing and de-flashing applications. Common industries include jewelry, cutlery, engine parts, fiberglass and the removal of graffiti or debris from wood, brick or stone.
The Evaluation Criteria
Each of these materials offers varying performance based on these characteristics, which you’ll need to consider when making your selection:
- Hardness: The Mohs Hardness Scale determines the material’s scratch resistance using a rating from 1 to 10. A higher rating means the media is more likely to scratch the surface, an important factor when preparing softer substrates.
- Surface profile: The abrasive’s size, shape, hardness and density combine to determine the profile it creates on the material’s surface. The result can be a no, low, medium or high etch.
- Surface removal: When choosing an abrasive media, you’ll need to know how much of the substrate’s surface the material will remove to ensure the result meets the project’s specifications.
- Recycling: If reducing costs is a concern for your business, consider whether you can recycle and reuse the material after abrasive media blasting.
- Working speed: Some materials enable you to complete the abrasive media blasting process faster than others.
- Bulk density: The abrasive’s density, measured in pounds per cubic foot, impacts its cleaning rate and the surface profile it leaves in the substrate.
Learn More About the Different Types of Abrasive Media
Finishing Systems offers several sandblast media types for sale. Many of our products are available in various grit sizes and packaging options to meet your company’s specific requirements. All these materials deliver the consistent quality and performance you need to maximize your projects’ outcomes.
Do you need assistance selecting from the different types of abrasive media? The Finishing Systems team has the experience and expertise to help you make an informed decision.
Contact us for more information or to get reliable answers to your abrasive media questions today.

